Lemon exports to the United Kingdom: a historic record for Morocco and a new commercial landscape
Morocco sets an unprecedented record by shipping 1,200 tonnes of lemons to the United Kingdom in less than a year, for a value of approximately one million dollars. This milestone surpasses the cumulative volume sent to this destination over the last decade, establishing a new benchmark for Moroccan citrus exports. After four years of contracting volumes, the recovery is clear and aligns with a broader strategy of upgrading quality and diversifying markets.
The ranking evolution is just as revealing: Morocco moved from 31st to 11th place among UK market suppliers in just a few months. This rapid progress shakes up a market traditionally dominated by Spain, South Africa, and Brazil. On UK shelves, Moroccan lemons regain visibility lost since the previous peak in the 2007/08 campaign, now surpassed by about 12% in volume according to sector data shared by specialized observers.
Behind this quantified achievement, the fundamentals align: logistical reliability via Tanger Med, complementary seasonality to the Spanish calendar, and ramped-up packaging stations meeting BRC/IFS standards. At a store in Manchester, a department head cited by an importer explains appreciating the “freshness and regular sizing” of Moroccan batches delivered in late winter, a sensitive window where supply regularity takes precedence over all other considerations.
Key figures reshaping the citrus map in the United Kingdom
The current momentum is part of a larger trend propelled by Moroccan fruits (raspberries, blueberries, mandarins, watermelon, avocado), whose sales in the UK are growing. Lemons fit into this trajectory, with an export value now exceeding one million dollars, according to the latest trade monitoring reports. The ripple effect results in new distribution contracts and assortment tests with British chains wishing to broaden their sourcing origins to reduce risks.
- 🍋 Rapid rise in supplier ranking: 31st → 11th ✅
- 📈 Value nearing 1.02 million dollars over ten months 💵
- 🚢 Efficient shipping window between November and August ⏱️
- 🤝 Strengthening partnerships with strategic British importers 🇬🇧
- 🧊 Stabilized cold chain along the Agadir–Tanger Med–UK corridors ❄️
| Period 📅 | Volume (t) 🍋 | Value (USD) 💵 | Supplier Ranking 🇬🇧 | Trend 📊 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007/08 | ~1,070 | ~0.85 M | Top 20 | 🟨 Previous record |
| 2018–2022 | Declining | Low | Beyond Top 25 | 🔻 Contraction |
| 2024/25 | 1,200 | ~1.02 M | 11th | 🟢 Record + recovery |
This breakthrough is not an isolated event. It reflects regained credibility that can extend to other references if operators maintain quality, supply consistency, and cost/value competitiveness. The first lesson for now: regularity pays off in a British market that has become more cautious yet eager for complementary origins.
The next step is to translate this momentum into quality jobs and sustainable investments, key issues at the heart of the Moroccan citrus chain.
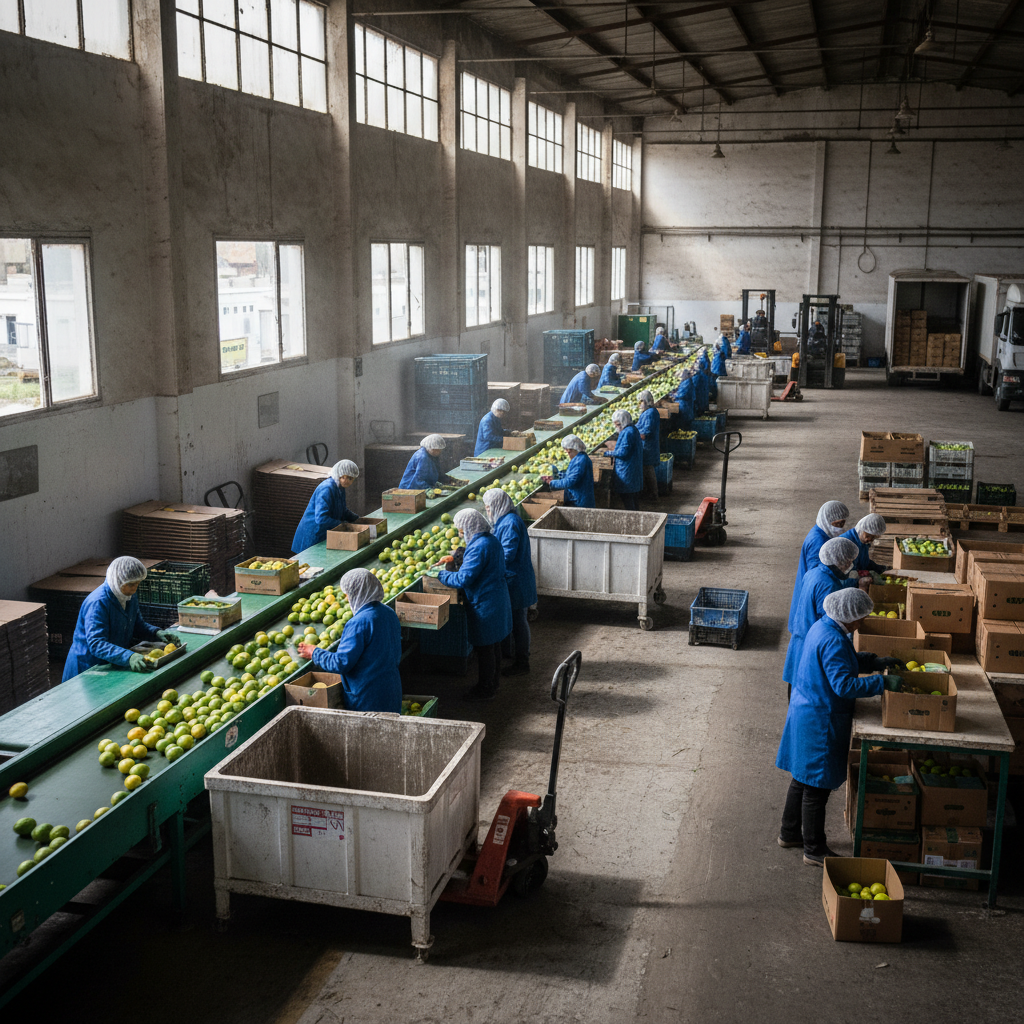

Employment and skills: impacts on agriculture, logistics, and territories
The record of lemon exports to the United Kingdom has direct impacts on the Moroccan economy, notably regarding employment. From the Souss-Massa orchards to the Gharb packaging stations, demand for qualified profiles is rising: optical sorting operators, quality controllers, cold technicians, HGV drivers trained in time management and anticipation of post-Brexit British inspections. At a fictional station, Atlas Citrus, the quality manager “Naïma” illustrates this upskilling: her team completed ONSSA–BRC modules to meet batch traceability requirements and MRL limits, reducing disputes at destination.
The multiplier effect is visible across the chain. Orchards recruit more for pruning and harvesting; stations create roles in maintenance and data (temperature recording, shipment number management); freight forwarders strengthen their planning teams to secure ferry and ro-ro ship slots. In Agadir, a transporter deployed IoT sensors for real-time temperature monitoring, allowing them to win two contracts with British retailers concerned about temperature stability over 72 hours of transit.
Priority skills and job quality
The development of lemons and other fruits destined for the UK requires cross-disciplinary skills. Agricultural operators must master low-pressure precision irrigation to limit water consumption, a critical issue in arid areas. Packaging teams learn to adjust waxing, sizing, and GS1 labeling, while sales staff train in hedging to cover GBP/MAD exchange risks. HR departments are urged to formalize seasonal contracts further, a key point for retention and workplace safety.
- 🧑🌾 Tense professions: facility drivers, optical sorting team leaders, energy/cold technicians.
- 🧪 Standards: BRC/IFS, GLOBALG.A.P., SMETA social audits to reassure UK buyers 🇬🇧.
- 🚛 Logistics: eco-driving, ferry planning, port slot management at Tanger Med.
- 💻 Digital: traceability ERP, GS1 labeling, IoT temperature monitoring.
- ⚖️ HR: formalized contracts, MSD prevention, gender equality at stations.
| Segment 🔗 | Key profiles 👩🔧 | Regions 🗺️ | Employment impact 👥 | Quality/Standards ✅ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orchards | Irrigation head, phytosanitary | Souss-Massa, Gharb | + seasonal | GLOBALG.A.P. 🍃 |
| Packaging | Optical sorting, QA, maintenance | Beni Mellal, Tadla | + qualified positions | BRC/IFS 🏷️ |
| Transport/Transit | HGV drivers, freight forwarders | Agadir, Tangier | + planning teams | ATP, cold chain ❄️ |
A British distributor cites three key elements for maintaining multi-year contracts: consistent quality, on-time delivery, and document compliance. In response, several Moroccan stations have created “compliance units” merging quality, export, and legal teams to anticipate regulatory changes. The most tangible result, according to a Casablanca-based freight forwarder, is a reduction in additional costs due to delayed departures and batch refusals.
Operational conclusion of this sequence: the record employment will be sustainable if based on skills, formalization, and investment in quality tools.
Competitiveness against Spain, South Africa, and Brazil: quality, schedule, and sustainability
Entering the Top 15 lemon suppliers to the United Kingdom requires competing with established players. Moroccan competitiveness is based on a triptych: complementary supply window, internationally recognized quality standards, and controlled costs thanks to geographical proximity and logistics efficiency. British buyers seek a “multi-origin” supply to cushion climate risks: in this scheme, Morocco can occupy the late winter and spring period when Spanish volumes fluctuate and South Africa has not yet fully resumed.
Sustainability becomes a purchasing criterion. Stations integrating water management, renewable energies, and plastic reduction earn points during audits. A cooperative in Berkane, for example, installed solar panels to stabilize the energy cost of the pre-cooling tunnel. Result: less thermal variability and fewer customer complaints. Commercially, index pricing with a fuel clause, set up by a Souss-Massa exporter, protects margins in periods of logistical volatility.
Concrete levers to secure Morocco’s position
To consolidate the lead, several levers stand out. Strict alignment with UK MRLs and digital phytosanitary documentation streamline port entries. Station specialization on a few key calibers reduces non-compliance rates. Finally, volume pooling via export platforms reduces per-unit freight costs and improves planning reliability.
- 🗓️ Targeted supply window: late winter → spring, premium slot.
- 🧼 Zero residue sought by some retailers: dedicated agronomic programs.
- ♻️ Water/Energy: drip irrigation, solar, wash water recovery.
- 📑 Document dematerialization: e-phyto certificates, batch-by-batch traceability.
- 💶 Freight-indexed negotiations: transparent revision clauses.
| Origin 🌍 | UK Window ⏱️ | Main advantage ⭐ | Key challenge ⚠️ | Morocco – Position 🎯 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spain | Autumn–winter | Proximity 🇪🇸 | Volume fluctuations | Complementarity 🟢 |
| South Africa | Summer–early autumn | Stable volumes 🇿🇦 | Distance | Season relay 🟢 |
| Brazil | Almost year-round | Availability 🇧🇷 | Cost + transit | Price/quality slot 🟢 |
| Morocco | Late winter–spring | Proximity + freshness 🇲🇦 | MRL, water | Consolidation underway ✅ |
This competitive differential, fueled by proximity and quality, positions Morocco as an agile partner with high potential to expand assortment. Next step: leverage this credibility to broaden the range.
This favorable terrain paves the way for a broader portfolio strategy where lemon serves as a springboard for other Moroccan references already on the rise.
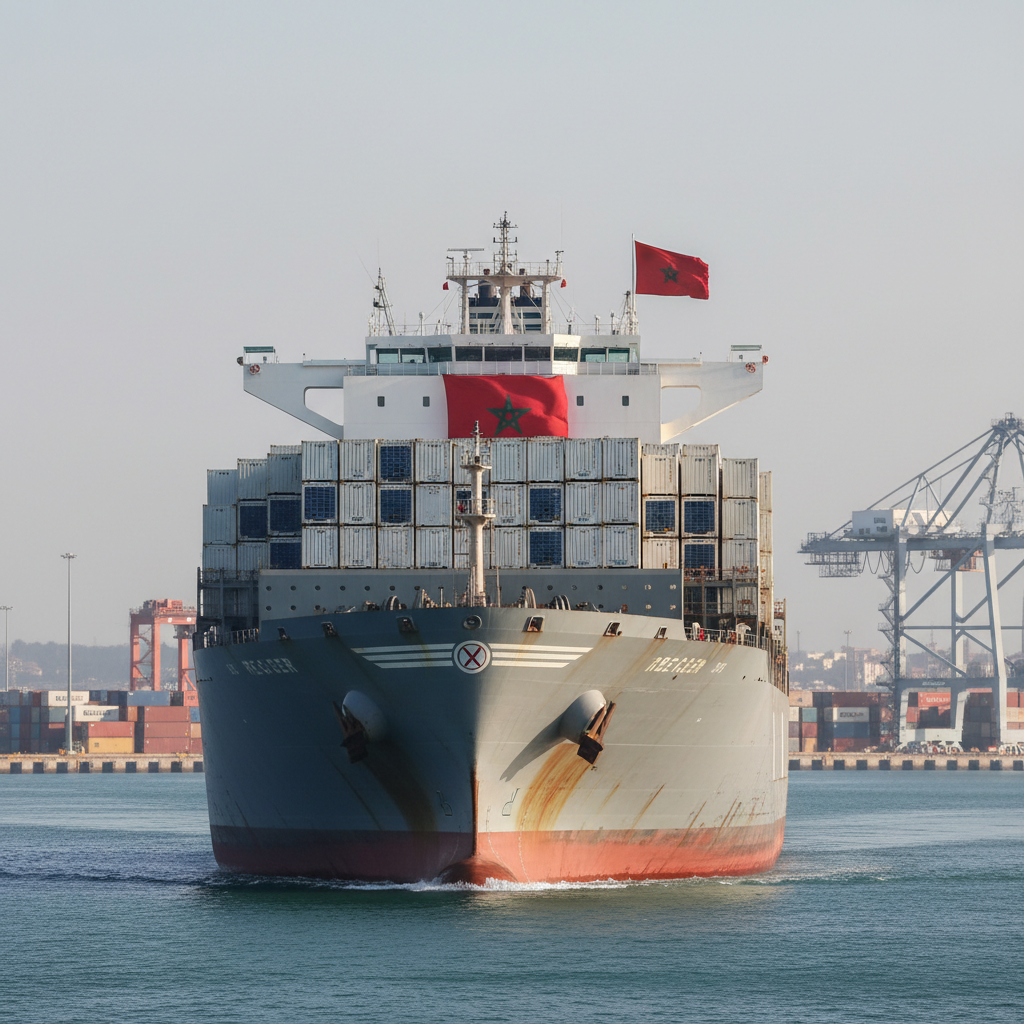

Winning portfolio: synergies between lemons, raspberries, onions, and tomatoes to strengthen presence in the UK
The success of lemons fits into a broader trend of strengthening Moroccan fruits and vegetables in the British market. Raspberries hit a new peak in the recent season with over 64,000 tonnes in global export and revenues of several hundred million dollars, boosting the reputation of Moroccan origin. On the vegetable side, onions bounced back after restrictions were lifted in summer 2024, and exporters opened new outlets, including in the Middle East, reinforcing operators’ financial resilience. As for tomatoes, Morocco ranks in the global top three with around 745,000 tonnes and nearly 1.2 billion dollars in revenues in the recent campaign, confirming the country’s structural competitiveness.
This product diversity offers logistical and commercial synergies. Exporters can fill truck returns and optimize cold use in multi-product transport. An Agadir logistician explains having combined lemon pallets with red fruit trays to maximize the economic footprint of the same convoy, reducing carbon footprint per kilo. Commercially, British buyers often prefer to partner with suppliers capable of serving multiple categories, which weighs positively in tenders.
Risk management and financing: the role of a multi-category portfolio
Operators combining citrus, red fruits, and early vegetables better dilute climate, health, and price uncertainties. Tomato cash flow, for example, can finance lemon quality investments (optical sorting, anti-mold systems), while raspberry margins cushion a potential watermelon downturn. Banks follow this reasoning: credit lines improve when the business plan relies on regular and diversified flows, with well-calibrated exchange hedging.
- 🧺 Balanced export basket: citrus + red fruits + early vegetables.
- 🔁 Logistical synergies: pooling trucks and cold storage.
- 💳 Smooth financing: cross cash flow, better banking conditions.
- 🛡️ Resilience: GBP/MAD exchange hedging and forward contracts.
- 📦 Customer value: one supplier, multiple categories, less risk.
| Product 🧺 | Reference volume 🚚 | Reference value 💵 | Role in mix 🎯 | UK trend 📈 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lemons | 1,200 t (UK) | ~1 M USD | Entry door 🇬🇧 | 🟢 Expansion |
| Raspberries | 64,400 t (global) | ~487 M USD | Origin brand | 🟢 UK appetite |
| Onions | 64,900 t | ~238 M USD | Buffer volumes | 🟢 Recovery |
| Tomatoes | 745,000 t | ~1.2 Bn USD | Financial foundation | 🟢 Solid |
Concretely, a Birmingham importer who tested Moroccan lemons extended his contract to mandarins and avocado trials. The lesson is clear: each product success strengthens origin credibility and opens other doors. The multi-reference portfolio is thus an accelerator of market access for the citrus sector.
This diversification strategy remains subject, however, to rules and contingencies that must be finely anticipated to sustain growth.
UK regulation, risks, and opportunities 2025: how to stay above one million dollars
Morocco’s performance happens in an evolving UK regulatory environment. Strengthened sanitary controls at entry, MRL compliance, and documentary requirements leave no room for slack. Operators who succeed internalize these constraints as operational standards and invest in digital traceability and electronic certificates. At the macro level, UK inflation eases but households remain cautious; this context favors origins offering a good quality/price ratio, a space where Morocco can thrive if logistics remain smooth and predictable.
Climate is a second critical parameter. Rainfall and temperature variability require ongoing investments in efficient irrigation, tolerant varietal selection, and integrated pest management. Some stations adopt natural post-harvest coatings to reduce losses and improve travel resilience. Others integrate solar energy to stabilize cold costs, meeting the ESG specifications of several UK retailers.
2025 scenarios and action plans for the lemon sector
The following scenarios help anticipate possible trajectories and identify measures to maintain the one million dollar threshold and aim beyond. They incorporate logistics, regulatory, and climate variables, as well as competitive dynamics with Spain, South Africa, and Brazil.
- 🟢 Controlled growth scenario: +10% volumes, stable quality, diversified UK clients → value increase.
- 🟡 Logistics volatility scenario: port/ferry delays → prioritize spot contracts and refrigerated stock buffers.
- 🔴 Climate stress scenario: water restrictions → focus on drought-resistant varieties, drip irrigation, harvest planning.
- 🟦 Adverse exchange scenario: falling GBP → hedging and quarterly price revision clauses.
- 🟣 Regulatory scenario: tightened MRLs → enhanced residue controls and agronomic itineraries.
| Scenario 🧭 | Main risk ⚠️ | Key measure 🛠️ | Monitoring indicator 📌 | Effect on value 💵 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controlled growth | Station capacity | Ship schedule + station OEE | OTIF > 95% ✅ | 🟢 +5 to +12% |
| Logistics volatility | Ferry delays | 48–72h cold buffer | Disputes < 1% 📉 | 🟡 Stable to -3% |
| Climate stress | Water | Drip irrigation + probes | kg/m³ water 🍃 | 🔴 -5 to -8% |
| Adverse exchange | GBP/MAD | Hedging + indexation | Coverage rate 📈 | 🟣 0 to -4% |
| Regulatory | MRL | Residue plan + e-phyto | Non-compliance 🚫 | 🟢 Neutralized |
Successful companies combine regulatory vigilance, operational excellence, and a value-based commercial vision. In practice, targeting a balanced client basket (retail + wholesalers + foodservice) and a controlled multi-origin offer (where relevant) smooths disruptions while protecting average price.
The message for the sector is clear: by securing quality, scheduling, and compliance, Morocco can sustainably maintain and surpass the one million dollar threshold for lemons in the UK while consolidating its reputation across all its agricultural exports.
Local value chain and client proximity: turning the record into a sustainable advantage
Turning a record into a competitive advantage requires aligning the entire value chain. Orchards optimize technical routes to preserve the juice and acidity sought by UK buyers. Stations invest in vision sorting to homogenize sizing and reduce presentation gaps. Freight forwarders set guaranteed slots departing from Agadir and Tanger Med to meet delivery windows of British logistics platforms.
This orchestration logic includes client proximity. High-performing exporters deploy bilingual teams, set up weekly quality checkpoints, and accept unannounced audits. A fictional company, “Noor Citrus,” opened a micro-commercial hub in London, enabling real-time communication with buyers and better understanding of store rotations. The result: fewer markdowns and finer restocking, improving the perception of Moroccan lemons among consumers.
Management indicators and performance culture
To endure, execution must be measured. Logistics KPIs (OTIF, transit time, thermal stability), quality (claims rate, MRL compliance), and commercial (average price, share of sales under contract) guide decisions. A Tadla station, for example, reduced its reconditioning rate by 20% by investing in a latest-generation sorting machine, amortized in one season thanks to labor savings and fewer disputes.
- 📦 OTIF > 95% and reconditioning < 3%: base targets to aim for.
- 🧊 Thermal gap < 1.5 °C in transit: freshness and shelf-life condition.
- 📑 100% document compliance rate: zero defects at UK entry.
- 💬 Continuous client feedback: short improvement loop.
- 🧭 Balanced client mix: retail, wholesale, foodservice.
| KPI 🎯 | Target threshold ✅ | Monitoring tool 🛠️ | Client benefit 🤝 | Margin impact 💹 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTIF | > 95% | TMS + ferry planning | Full shelves 🛒 | 🟢 Average price ↑ |
| MRL compliance | 100% | LIMS + audits | UK trust 🇬🇧 | 🟢 Reduced disputes |
| Thermal gap | < 1.5 °C | IoT sensors | Freshness 🍋 | 🟢 Reduced waste |
| Reconditioning | < 3% | Optical sorting | Stable presentation | 🟢 Reduced costs |
Ultimately, rigorous professionalization, client proximity, and investment in quality are the pillars transforming a one-off achievement into a lasting competitive advantage. These same pillars will strengthen Morocco’s position in the international citrus trade.
{“@context”:”https://schema.org”,”@type”:”FAQPage”,”mainEntity”:[{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”Why is it said that Moroccan lemons set a record in the United Kingdom?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”Because Morocco shipped about 1,200 tonnes to the United Kingdom in less than a year, for a value close to one million dollars. This volume exceeds the cumulative of the previous decade and breaks the 2007/08 peak, propelling the country from 31st to 11th supplier ranking.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What are the employment impacts in Morocco?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”The export increase supports jobs in orchards (pruning, harvesting), stations (sorting, quality, maintenance), logistics (drivers, freight forwarders), and compliance (document control). Skill needs rise in the cold chain, traceability, and BRC/IFS standards.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”How does Morocco stay competitive against Spain and South Africa?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”By betting on a complementary supply window, geographic proximity, consistent quality, controlled logistics costs, and strong compliance with UK standards (MRLs, audits). Sustainability (water, energy, packaging) is an additional asset.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”Can this success benefit other Moroccan products?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”Yes. The gained credibility facilitates contracts for neighboring categories (mandarins, raspberries, blueberries, avocados). Logistic pooling reduces costs and enhances the commercial attractiveness of a multi-reference supplier.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What is the main risk to watch in 2025?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”The combination of logistics volatility, water stress, and regulatory tightening. Operators investing in cold chain, digital traceability, and efficient irrigation are best placed to sustainably exceed one million dollars on the UK market.”}}]}Why is it said that Moroccan lemons set a record in the United Kingdom?
Because Morocco shipped about 1,200 tonnes to the United Kingdom in less than a year, for a value close to one million dollars. This volume exceeds the cumulative of the previous decade and breaks the 2007/08 peak, propelling the country from 31st to 11th supplier ranking.
What are the employment impacts in Morocco?
The export increase supports jobs in orchards (pruning, harvesting), stations (sorting, quality, maintenance), logistics (drivers, freight forwarders), and compliance (document control). Skill needs rise in the cold chain, traceability, and BRC/IFS standards.
How does Morocco stay competitive against Spain and South Africa?
By betting on a complementary supply window, geographic proximity, consistent quality, controlled logistics costs, and strong compliance with UK standards (MRLs, audits). Sustainability (water, energy, packaging) is an additional asset.
Can this success benefit other Moroccan products?
Yes. The gained credibility facilitates contracts for neighboring categories (mandarins, raspberries, blueberries, avocados). Logistic pooling reduces costs and enhances the commercial attractiveness of a multi-reference supplier.
What is the main risk to watch in 2025?
The combination of logistics volatility, water stress, and regulatory tightening. Operators investing in cold chain, digital traceability, and efficient irrigation are best placed to sustainably exceed one million dollars on the UK market.




Comments are closed