A new era for Moroccan defense: the 2026 agreement with Israel
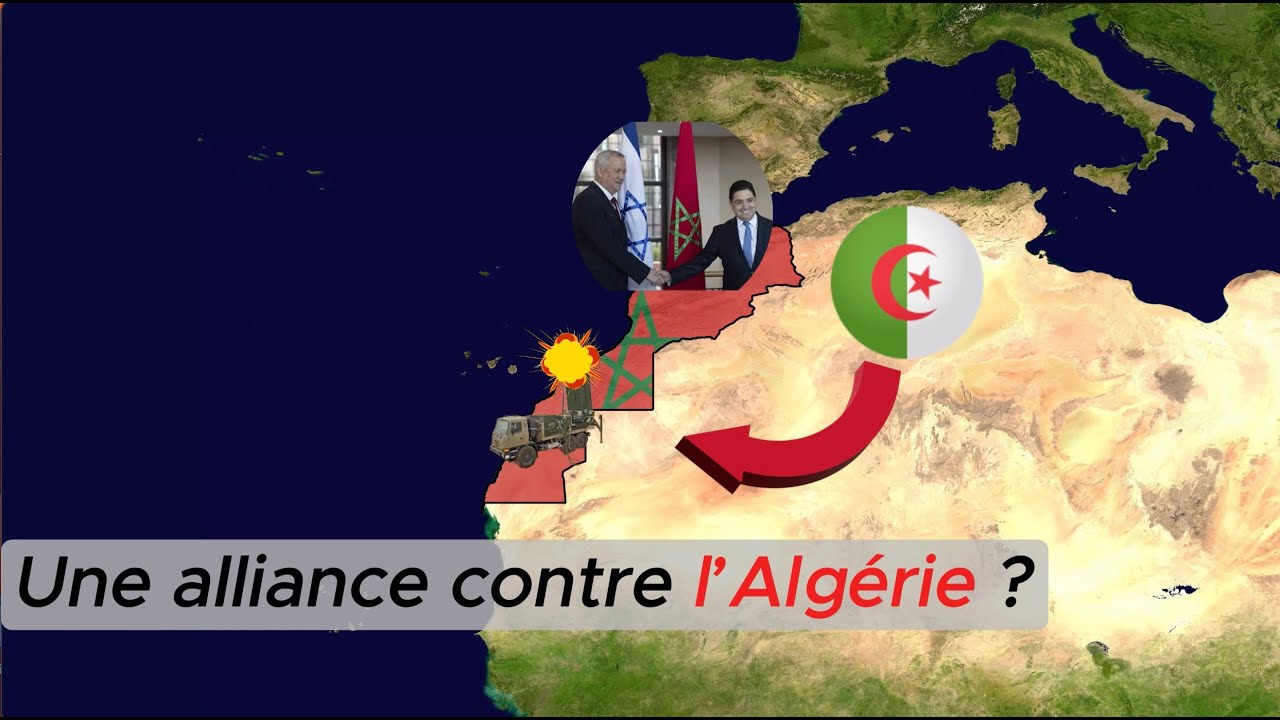
The year 2026 marks a decisive turning point in the military history of the Kingdom. Five years after the resumption of diplomatic relations under the aegis of the Abraham Accords, Morocco and Israel have just formalized a joint working plan for defense. This agreement, signed in Tel Aviv during the last session of the joint military committee, is not content with symbols: it establishes a structured and lasting military cooperation.
This strategic rapprochement responds to a clear desire from Rabat to modernize its security apparatus in the face of regional challenges. Closed-door meetings between senior officials of the IDF and the Royal Armed Forces (FAR) led to a roadmap that goes beyond mere equipment acquisition. It now involves strategic planning, intelligence sharing, and long-term force development. In a context where the stability of the Western Sahara remains an absolute priority for Moroccan diplomacy, this technological support offers an undeniable qualitative advantage.
A major technological shift: from buyer to strategic partner
The most striking evolution in recent years lies in the diversification of the Kingdom’s suppliers. Historically linked to American and European equipment, Morocco is making a calculated transition towards Israeli technology, known for its cutting edge in cyber defense and surveillance. This change of course is not insignificant; it aims to strengthen the strategic autonomy of the FAR.
Recent acquisitions testify to this rise in power. The Barak MX air defense system and reconnaissance satellites now provide Morocco with an unprecedented surveillance capacity. More concretely, the agreement includes the integration of ATMOS 2000 self-propelled artillery systems, produced by Elbit Systems. This contract, estimated at around 200 million euros, equips Moroccan artillery with 155 mm truck-mounted cannons, capable of hitting targets over 40 kilometers away with surgical precision thanks to digital fire control systems.
These equipments require top-level logistics and human infrastructure. Modernization does not stop at the battlefield borders; it also involves upgrades in training centers and support structures, reflecting the excellence sought by institutions like the military hospital of Meknès, which plays a key role in operational and health support for the troops.

Israel extends its military influence in Africa via the Moroccan pivot
For the Hebrew State, this strategic partnership goes beyond the bilateral framework. Israel sees Morocco as a key gateway to North and West Africa. As the Sahel region is plagued by chronic instability, marked by militant group activity and trafficking networks, Morocco’s geographical position is a major asset for regional security.
By institutionalizing its ties with Rabat, Tel Aviv extends its security footprint far beyond the Eastern Mediterranean. This alliance helps counter the influence of other geopolitical actors in the area and consolidate alliances against common threats. 🌍 This dynamic fits into a logic where geopolitics and economic interests intersect: securing borders also means securing emerging markets in West Africa.
However, this rise in power must be analyzed with lucidity. It occurs in a sometimes tense regional climate, notably due to the latent conflict between Morocco and Algeria. The acquisition of cutting-edge technologies by Rabat modifies the balance of power and forces neighboring actors to revisit their own defense doctrines.
The pillars of the Morocco-Israel cooperation by 2026
This joint working plan is not limited to commercial transactions. It rests on several fundamental axes aiming to create interoperability between the two armies. Here are the key areas of this reinforced collaboration:
* 📡 Intelligence and Cyber Defense : Sharing critical information and training on digital threats.
* 🚀 Air and Anti-missile Defense : Deployment of technological shields to secure national airspace.
* 🎯 Precision Artillery : Modernization of fire with automated systems like the ATMOS 2000.
* 🏭 Industrial Cooperation : Local maintenance projects and transfer of technological skills.
* 🤝 Joint Training : Regular military exercises to align operational procedures.
The table below illustrates the evolution of Morocco’s acquisition priorities, marking the shift from a traditional fleet to a connected army:
| Equipment Domain | Traditional Approach | New Strategy (Israel Partnership) |
|---|---|---|
| Surveillance | Classic ground radars | Spy satellites and tactical drones |
| Artillery | Manual towed cannons | Self-propelled systems (ATMOS 2000) 💥 |
| Air Defense | Short-range systems | Multi-layer shield (Barak MX) |
| Maintenance | Foreign subcontracting | Development of local capabilities |
The challenge for Morocco is twofold: ensure its sovereignty through deterrence and stimulate a national defense industrial ecosystem. By partnering with Israeli expertise, the Kingdom aims to become a regional hub for military maintenance and production, thereby creating added value and opportunities for Moroccan engineers and technicians.
This dynamic confirms that Morocco no longer positions itself merely as a client, but as a central actor in the new architectures of security and alliances emerging between the Mediterranean and sub-Saharan Africa.
What are the main equipments acquired by Morocco from Israel?
Morocco notably acquired the Barak MX air defense system, surveillance drones, spy satellites, and the ATMOS 2000 self-propelled artillery system.
Why is this 2026 agreement strategic for Israel?
It allows Israel to extend its military influence in North and West Africa, using Morocco as a stable partner to counter regional threats and instability in the Sahel.
What is the economic impact of this cooperation for Morocco?
Beyond security, this agreement targets technology transfer and the development of a local defense industry, creating opportunities for qualified Moroccan labor in maintenance and engineering.
Since when have military relations resumed?
Cooperation accelerated following the normalization of diplomatic relations in December 2020 within the framework of the Abraham Accords, reaching an institutional level with the 2026 working plan.


No responses yet