Five years have passed since the normalization of diplomatic relations between Rabat and Tel Aviv, sealed under the Abraham Accords. What began as a diplomatic opening has transformed into a true multisectoral strategic alliance. At the heart of this dynamic, military cooperation continues to intensify, as evidenced by the recent signing of a joint action plan for the 2026 horizon.
This roadmap, validated during the third meeting of the joint military committee in Tel Aviv, marks a decisive turning point. Far from being limited to mere ceremonial exchanges, Morocco and Israel are entering an operational phase focused on high technology and the defense industry. For economic and geopolitical observers, it is clear that the Kingdom seeks to consolidate its position as a regional pivot while navigating a complex international context.
A security alliance scaling up by 2026
Cooperation between the Royal Armed Forces (FAR) and the Israeli army has reached a new level. Recent discussions no longer focus solely on equipment purchases but on deeper strategic integration. According to experts, the goal is now technology transfer and the joint development of advanced defense systems. Steven Höfner, head of the Konrad Adenauer Foundation office in Morocco, points out that the two partners aim to develop drones and air defense systems, including satellite technology.

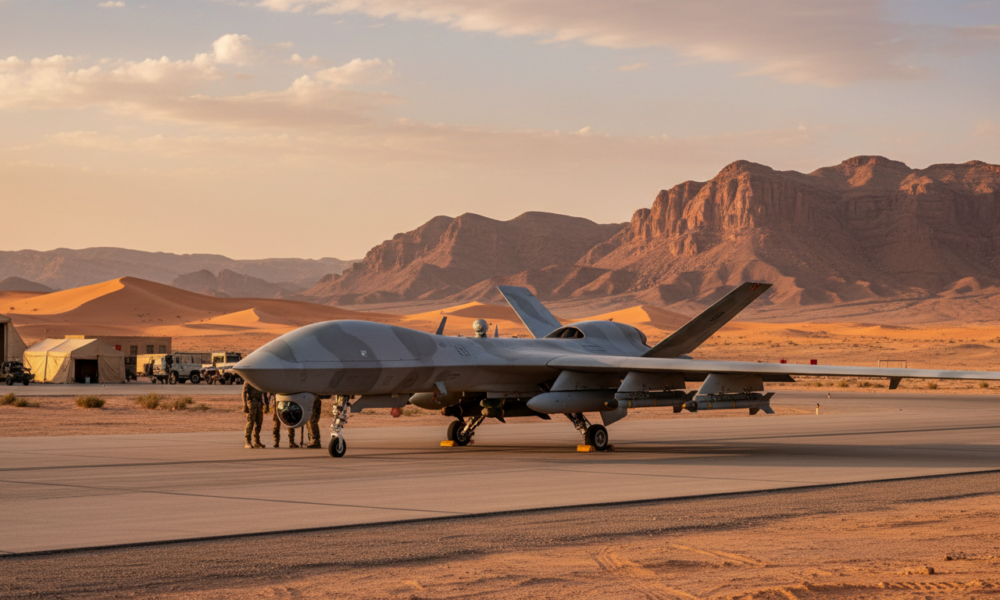
This technological upgrade meets rapid modernization imperatives. Morocco, historically one of the main arms importers in Africa, has diversified its suppliers. While the United States and France remain indispensable partners, the Hebrew state has risen, according to SIPRI data, to become the Kingdom’s third largest supplier over the 2020-2024 period. This diversification allows Rabat to reduce its dependency while gaining access to cutting-edge equipment, especially in intelligence and electronic warfare.
The shift towards local military industrialization
Moroccan ambition goes beyond simple off-the-shelf acquisition. The 2026 work plan emphasizes the establishment of production units on national soil. Israeli military influence in Morocco is now reflected in concrete industrial projects, notably the manufacture of kamikaze drones and surveillance systems. This strategy aims to create an autonomous defense ecosystem, capable of generating local added value and positioning Morocco as a regional export platform in the medium term.
Here is an overview of the key areas of this technological cooperation:
| Cooperation Field 🛡️ | Type of Equipment / Technology | Strategic Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Air Defense | Barak MX systems, Iron domes (negotiations) | Securing national airspace |
| Drones & UAV | Heron, Harop (loitering munitions) | Border surveillance and targeted strikes |
| Intelligence | Observation satellites, Cyber defense | Information autonomy and anticipation |
Regional tensions and major diplomatic issues
This strengthening of military capabilities is not happening in a geopolitical vacuum. It is taking place in a context of persistent rivalry with neighboring Algeria. The acquisition of breakthrough technologies gives Morocco an undeniable qualitative advantage, altering the balance of power in the Maghreb. Simon Wolfgang Fuchs, researcher at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, notes that thanks to Israeli imports, the Moroccan army has modernized considerably, technologically surpassing its regional rival in certain specific segments.
However, Algiers continues to arm massively, notably from Russia, fueling an arms race that worries Western chancelleries. The latent conflict between Morocco and Algeria, crystallized around the Sahara issue, remains the main driver of this security doctrine. For Rabat, Israel’s recognition of its sovereignty over the Sahara, following the United States, represents a major diplomatic victory which justifies, in the eyes of decision-makers, maintaining these ties despite regional turmoil.
Public opinion facing realpolitik
While the state pursues its strategic roadmap, Moroccan civil society remains divided by conflicting currents. Historical solidarity with the Palestinian cause remains strong, and the tragic events in Gaza have revived criticism of normalization. Demonstrations calling for a break in relations reflect a gap between state strategy and popular sentiment. The government must therefore navigate cautiously, maintaining the course of its national interests while managing street pressure.
This internal stability is nonetheless crucial for the economy. A peaceful security climate enables the state to focus on its development projects and support employment. It is within this framework of stability that large public hiring campaigns are organized, such as the 2025 career opportunities and recruitment competitions at the Ministry of National Education, which aim to strengthen the country’s social fabric.
Beyond weapons: a pragmatic economic cooperation
It would be reductive to limit this relationship to security aspects only. The economic benefits are real, although tourism has suffered from the war context in the Middle East, with direct flights suspended. Opportunities are shifting towards sectors with higher added value and vital to the Kingdom’s future.
Agriculture and water management are top priorities. Faced with structural water stress, Morocco draws on Israeli expertise in desalination and precision irrigation. At the same time, while Morocco orders helicopters and heavy equipment for its defense, it is also negotiating partnerships to valorize its phosphates, essential for fertilizer production needed by Israeli agriculture. It is a mutually beneficial exchange: food security in return for territorial security.
Economic development axes notably include:
- 💧 Water management: Wastewater recycling technologies and drip irrigation.
- 🌱 Agritech: Crops adapted to arid environments and resistant seeds.
- 🔬 R&D: University collaboration and technology know-how transfer.
- 🔋 Energy: Potential projects in renewable energies and green hydrogen.
What are the objectives of the 2026 military plan between Morocco and Israel?
This plan aims to structure operational cooperation, strengthen joint exercises, and especially accelerate the development of defense industrial projects in Morocco, notably in the fields of drones and satellite surveillance.
What is the impact of tensions in Gaza on this cooperation?
Although tensions have caused strong opposition within Moroccan public opinion and a slowdown in tourism, strategic and military relations between the two states continue, motivated by national security issues and the Sahara question.
Does Morocco depend solely on Israel for its armament?
No, Morocco maintains a diversification strategy. Although Israel has become the third supplier in the recent period, the United States and France remain the historical partners and main providers of heavy equipment such as fighter jets and armored vehicles.
How does Algeria react to this rapprochement?
Algiers perceives this alliance as a direct threat to its national security. In response, Algeria strengthens its own military capacities, mainly via Russian purchases, which maintains a climate of tension and an arms race in the Maghreb region.


No responses yet