United Nations and American Initiative: a Sahara Resolution That Reshuffles the Cards of the Western Sahara Conflict
In New York, momentum has accelerated around the Western Sahara conflict with a project supported by Washington at the United Nations Security Council. The submitted text aims to clarify the political path by setting Sahrawi autonomy under Moroccan sovereignty as the central reference. This approach, consistent with positions already expressed within the UN, fits into a sequence where Moroccan diplomacy has multiplied signals of dialogue with international partners and economic actors. Why is this agenda so interesting to HR professionals and decision-makers in Morocco? Because geopolitical clarity conditions investments, and therefore employment.
The voting project on MINURSO, traditionally routine, now integrates a status issue. According to the text distributed to Council members, the 2007 Rabat initiative becomes the most “serious and realistic” basis. This formulation, debated on the international relations stage, is contested by the Polisario Front, which recalls its attachment to the principle of self-determination. Beyond posturing, the heart of the discussion concerns the effectiveness of a political solution capable of opening development prospects. For Moroccan companies, legal and institutional visibility is a tangible lever: site planning, contract security, multi-year recruitment.
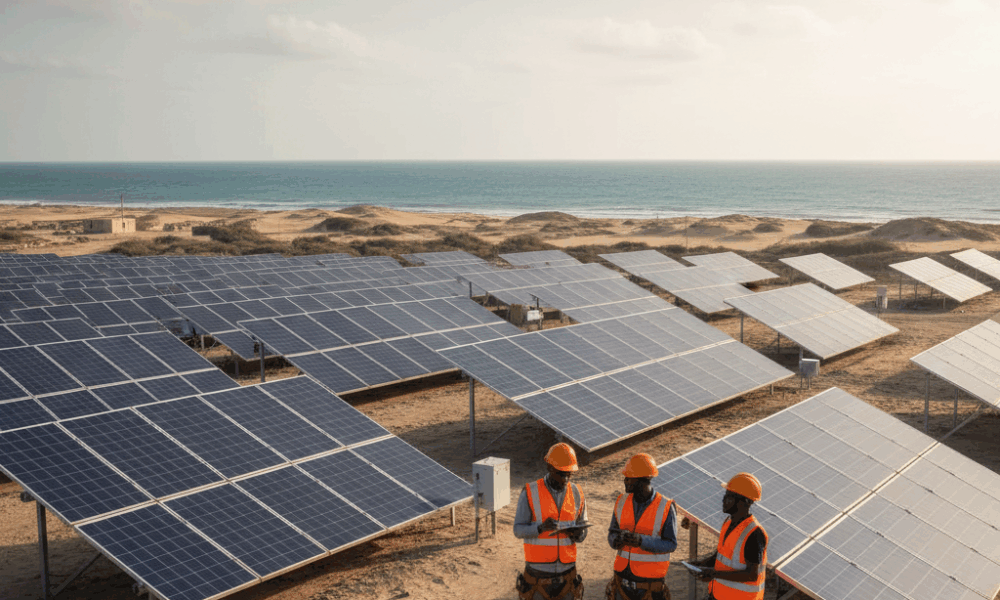
In this context, American officials, including former leaders, have publicly reaffirmed their support for the Moroccan approach. The influence of Washington as “penholder” on the file at the Security Council strengthens the idea of a resolution that favors a gradual exit from the status quo. This orientation is closely followed by investors and HR departments, especially those considering new bases in Dakhla or Laâyoune. One example speaks to all: a Moroccan logistics group, “SaharaTech Logistics,” has revised its recruitment plan over three years, conditioning the opening of 250 positions on the normative stabilization carried by the future Sahara resolution.
Short-term impacts are already visible in talent requests: compliant profiles, international economic law lawyers, QHSE managers, purchasing managers mastering UN clauses, not forgetting experts in procurement. HR departments also anticipate transversal needs: data analysts for forecasting port flows, wind and solar technicians, maintenance managers, and site managers. A useful documentary base to understand the international framework of autonomy is available via this dedicated analysis that synthesizes the doctrine and its sectoral impacts.
Key Landmarks to Decipher the UN Sequence
To better navigate, it is useful to clarify some notions and milestones. The MINURSO mandate is renewed annually, but the current edition aims to integrate an additional political signal. Discussions at the UN focus on the centrality of the autonomy initiative and the terms framing negotiations between parties. Moroccan diplomacy seeks clear language that secures investors’ ground and strengthens the socio-economic integration of the southern provinces.
- 🧭 Course clarification: Sahrawi autonomy under Moroccan sovereignty as the crisis exit reference.
- 🤝 Political dialogue: trust mechanisms encouraged between Rabat and the parties, with UN mediation.
- 🏗️ Employment effect: increased visibility for port sites, energy, and services, thus recruitment needs.
- 🛡️ Risk management: consideration of the Polisario Front positions in operational assessment.
- 📊 HR governance: skill upgrading on international compliance and ESG reporting.
| Milestone 🗓️ | Actor 👥 | Key content 🔑 | Job signal 💼 |
|---|---|---|---|
| UN text project | Washington | Explicit support to Sahrawi autonomy | Opening of positions in compliance and public affairs |
| MINURSO Renewal | United Nations | Mandate + political dimension | Three-year plan for operational recruitments |
| Rabat Position | Moroccan diplomacy | Stability, Moroccan sovereignty | Attraction of investments and local careers |
| Reservations | Polisario Front | Disagreement on the method | Need for risk management specialists |
The main takeaway is simple: a clearer political direction creates solid foundations for the real economy, and thus for employment. The next section precisely explores these sectoral fallouts.

Sahrawi autonomy and Moroccan sovereignty: economic and HR effects in the southern provinces
Assuming the Sahara resolution confirms the centrality of Sahrawi autonomy, the knock-on effects on Moroccan employment could be significant. Dakhla and Laâyoune are already in an acceleration phase: port infrastructures, fish processing zones, renewable energies, sports tourism, health services, and digital ecosystems. The common denominator: a demand for talents adapted to large-scale projects and international standards. The example of “SaharaTech Logistics” illustrates these dynamics: the company planned 250 recruitments over 36 months, prioritizing operational profiles (operations agents, maintainers, quality controllers) and managers (supply chain, FIDIC contract lawyers, data planners).
For candidates, orienting towards promising sectors becomes strategic. The upgrading of services calls for specific jobs: solar farm technicians, QHSE supervisors, maritime planners, industrial refrigeration experts for the fish chain. Companies, for their part, invest in employer branding and continuous training. A useful resource to map skills and build an action plan is the ANAPEC SKILLS guide, which details bridges between sectors and emerging professions. To position themselves with major employers, opportunities also exist in telecoms and automotive: see for example the announcements of Maroc Telecom and the SMEIA Group.
Moroccan diplomacy has also favored balanced regional integration, supporting logistics towards West Africa. This projection translates into needs for trilingual profiles (Arabic-French-English), international buyers, project management controllers, and export compliance managers. International donors and investors pay attention to ESG standards, supply chain traceability, and anti-corruption mechanisms. Result: HR departments structure compliance officer positions and internal audit cells, with an increasing emphasis on data governance.
- ⚓ Ports and logistics: operations agents, terminal managers, maritime planners.
- 🌞 Renewable energies: solar technicians, wind engineers, maintenance supervisors.
- 🐟 Fisheries and agro-processing: refrigeration experts, quality managers, export managers.
- 🏨 Tourism and services: hotel managers, digital marketers, specialized guides.
- 🧪 Health and biotech: lab technicians, trial coordinators, biomedical engineers.
| Sector 🚀 | In-demand Jobs 👩💻 | Key Skills 🧩 | Useful Resources 🔗 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics | Planning, customs, data planning | Incoterms, EDI, Power BI | Urban planning and engineering 🏗️ |
| Energy | Solar/wind maintenance | HSE, CMMS, IEC standards | Reference employers 🌟 |
| Fisheries | Quality, cold chain | HACCP, ISO 22000 | Dynamic territories 🌊 |
| Telecoms | Network supervision, data | ITIL, scripting | Job openings 📶 |
To accompany these developments, public actors strengthen employability through competitions and integration schemes. Candidates can learn about administrative procedures and sectoral competitions through this practical guide on health competitions. Signals are converging: political clarity, investments, and talent needs. The next step concerns training, addressed below.
HR fallouts take full dimension when skill upgrading follows the pace of projects. Heading towards training and sectors.
Skills, training, and health: building careers anchored in Moroccan sovereignty
The skills axis is decisive to transform a diplomatic direction into concrete opportunities. Observed needs in the southern provinces favor agility, compliance, and technical know-how. Moroccan and private institutions respond with a structured offer: universities, sectoral institutes, hospitals, and laboratories. The objective: secure industrial projects and improve access to care, two conditions for attractiveness for talents and their families.
On the academic side, bridges open between engineering, data, law, and management. The assets of a hybrid path are clear: an energy engineer with a minor in public contracts law better meets donors’ specifications. Moroccan establishments adapt their recruitments and programs. For example, the International University of Rabat strengthens its teams and laboratories, as shown by this announcement of 37 new talents. In health, the extension of care offerings accompanies the demographic growth of the southern provinces and professional mobility.
The hospital network strengthens thanks to reference actors and practical training institutes: consult the services of the Rabat Clinic to understand the standards, the offerings of the IFPS for paramedical professions, or the programs of the Pasteur Institute of Morocco for research and epidemiological surveillance. Public and para-public recruitments remain an important outlet: candidates can follow procedures via the CNSS jobs portals and the health sector competitions mentioned above.
- 📚 Hybrid paths: combining technical, legal, and data skills to answer tenders.
- 🩺 Health professions: specialized nurses, imaging technicians, biomedical engineers.
- 🔐 Compliance/ESG: mastery of standards, internal audit, sustainable reporting.
- 🧪 Biotech/labs: quality, biosecurity, critical equipment management.
- 🌐 Languages and soft skills: international negotiation, ethics, intercultural management.
| Skill 🎯 | Certification/Path 📄 | Where to train 🏫 | Outlets 2025+ 🌱 |
|---|---|---|---|
| International compliance | ISO 37001, ISO 19600 | ANAPEC SKILLS | Compliance officer, ESG auditor ✅ |
| Renewable energies | HSE, CMMS, IEC | Engineering schools, professional centers | Maintenance, operation 🔧 |
| Health professions | Competitions, specialization | IFPS, Rabat Clinic | Hospitals and clinics 🏥 |
| Biomedical research | Good lab practices | Pasteur Institute Morocco | Labs, quality control 🧫 |
For illustration, “Nadia,” HR manager in Laâyoune, set up a work-study path for solar maintenance technicians: 6 months of workshop training, 6 months on-site, mentoring by a senior engineer, and preparation for HSE certification. Result: 82% insertion at 12 months. The message is clear: with consolidated Moroccan sovereignty, the battle is won through skill.

Strategic reading for recruiters: from Washington to employment grounds, turning the advantage
Washington‘s position at the UN acts as a confidence multiplier for investors and funders. For recruiters, the subject is not theoretical: it involves workforce architecture, risk mapping, and contract compliance. Three action angles emerge: securing international paths; aligning HR policies with ESG standards; building continuous regulatory monitoring. For example, companies deploying American or European skills on southern sites will benefit from organizing mobility through clear channels, including visa procedures via the BLS Rabat center when external teams are involved.
Methodologically, a quarterly compliance review becomes essential: contractual resilience clauses, third-party mapping, ethical alert channels, supplier due diligence. The reinforcement of the economic rule of law sought by Moroccan diplomacy translates into greater demands on actor probity. Recruiters can rely on national benchmarks to optimize processes, like the recommendations of the HCP on hiring optimization. Technical departments, meanwhile, lean on reference bodies to ensure testing and quality control, consulting for example the best practices for recruitment at LPEE.
- 🧭 Risk mapping: integrate geopolitical variables and the Polisario Front stance in the continuity plan.
- 🧑⚖️ Contractual compliance: anti-corruption clauses, traceability, audit mechanisms.
- 🌱 ESG and attractiveness: extra-financial reporting, equal opportunity, workplace safety.
- 🌍 International mobility: visa procedures, occupational health, family support.
- 🔎 Regulatory monitoring: follow-up of United Nations decisions and their local transposition.
| Domain 🧱 | Priority actions ✅ | Tools/resources 🧰 | Employment impact 💥 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance | Due diligence, ethical alerts | ISO standards, internal audits | Creation of compliance positions 👩⚖️ |
| Mobility | Visa procedures, insurance | BLS Rabat | Attraction of international talents ✈️ |
| Monitoring | UN follow-up, consultations | Autonomy file | Proactive HR decisions 📈 |
| Security | Inter-state coordination | Security cooperation | Operational continuity 🛡️ |
One last often underestimated lever: the employer brand. In a transforming area, sharing career paths, salary progression, work condition quality, and societal impact makes a difference. Testimonial videos and campus roadshows support candidates’ trust. To inspire these approaches, a cross-view on the best recruiters’ practices is available via the ranking of top employers in Morocco.
Companies transforming the geopolitical signal into a sustainable HR advantage take the lead. What remains is understanding the connection with the public service and territories.
Governance, public employment, and territories: what concrete UN effects on careers and recruitments?
If the path of Sahrawi autonomy is established in practice, local administration and public services in the southern provinces will continue capacity building. This means recruitment programs in education, health, equipment, justice, and social services. Candidates will be able to claim transversal skills: public project management, procurement, internal control, budget steering. Social organizations play a central role, such as the National Social Security Fund; procedures are detailed on the apply to CNSS page. Health competitions constitute another structuring channel, accessible via this competition guide.
Territorial logic also implies partnerships with public companies and reference laboratories to secure projects. The recruiting practices at LPEE can inspire candidates from the dossier preparation stage: clarity of experiences, measurable results, certifications. Likewise, optimizing hiring processes in administrations and public companies can rely on HCP recommendations. Finally, the circulation of skills between regions will remain an issue: temporary mobility to Tangier, Casablanca, or Rabat, according to project needs and work-study training.
- 🏛️ Local public employment: administrators, territorial engineers, management controllers.
- 🏥 Health and social: general practitioners, nurses, social workers, hospital executives.
- 🧱 Infrastructure: project managers, construction technicians, site quality managers.
- 📈 Public finance: accountants, controllers, internal auditors.
- 🗣️ Legal affairs: contract management, mediation, institutional communication.
| Political scenario 🔮 | Effect on public employment 👔 | Skills sought 🧠 | Practical resources 🧭 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Text adoption | Acceleration of recruitments | Project management, public procurement | CNSS • HCP ✅ |
| Amendments | Gradual progression | Compliance, reporting | UN folder 📘 |
| Blockage | Targeted recruitments | Risk management | Engineering 🏗️ |
A point of attention: territorial cohesion requires the presence of attractive health and education services. Concrete tracks exist through the IFPS and the Pasteur Institute Morocco to train and retain paramedical and scientific talents. Mobility towards other employment basins, like the Tangier-Assilah corridor, can also complement career paths. Ultimately, the articulation between UN orientation and localized employment policies is evaluated by a simple indicator: the quality of services rendered to citizens, hence the capacity to attract and retain qualified professionals.
Value chains, SMEs and investments: translating Moroccan diplomacy into contracts and sustainable jobs
Value chain competitiveness depends as much on diplomatic decisions as on operational execution. If the political signal from the United Nations consolidates visibility, the relay is taken by SMEs, mid-sized companies, and investors. Transformation projects – fisheries, energies, tourism, construction – require structured local suppliers and integration capacity. The Moroccan ecosystem organizes itself: public-private consortiums, logistics hubs, shared service centers, accelerators for upgrading. Purchasing departments encourage supplier qualification, certification, and the adoption of digital standards for order tracking.
To stimulate investment and employment, some companies look towards agri-food and industrial partnerships with foreign actors. Inspirations exist, such as implantation strategies described in this experience feedback on an agri-food investment in Brittany or on multilateral security cooperations useful for business continuity (examples Morocco–Thailand–France). These cases help structure concrete roadmaps: performance clauses, logistical pooling, compliance, local impact indicators. Regarding recruitment, emphasis is placed on technical jobs, middle management, and international B2B sales.
Employment dynamics are also visible sector-wise. Telecoms, automotive, and urban engineering are strengthening, backed by recruiting actors: consult opportunities at SMEIA Group, job openings at Maroc Telecom, and urban engineering projects presented by NOVEC. Candidates would benefit from following simple indicators: order book, partnerships concluded, tenders won, investments validated. Recruiters, meanwhile, map shortages and bet on work-study, referral, and interregional mobility.
- 🧱 Local integration: favor certified suppliers and joint training.
- 🔗 Supply chain: digitize traceability and strengthen quality.
- 🤝 International partnerships: skills transfer and local recruitment clauses.
- 📈 Impact KPIs: jobs created, retention rate, share of local purchases.
- 🧑💼 HR upgrading: middle management, support functions, business development.
| Value chain 🔧 | 2025 Priorities 📌 | Targeted profiles 🧑🏭 | Resources 📚 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fisheries | Cold, quality, export | Quality managers, logisticians | ANAPEC 🎓 |
| Energy | Maintenance, HSE | Supervisors, technicians | Employer benchmarks 📊 |
| Telecoms | Network resilience | NOC engineers, data | Recruitments 📶 |
| Construction/Urbanism | Quality, deadlines | Project managers, quantity surveyors | NOVEC 🏗️ |
In sum, the economic translation of the UN signal depends on the capacity of Moroccan companies to execute quickly and well, while strengthening local employability. The alignment between Moroccan diplomacy and entrepreneurial networking produces sustainable jobs when supported by training, compliance, and innovation.
{“@context”:”https://schema.org”,”@type”:”FAQPage”,”mainEntity”:[{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What does the American initiative at the UN change for the Moroccan labor market?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”It brings political visibility to the file, placing autonomy under Moroccan sovereignty as a reference. This visibility encourages investments in the southern provinces and creates immediate needs in compliance, engineering, logistics, health, and services.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”Which sectors will recruit primarily if the resolution progresses?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”Port logistics, renewable energies, fisheries, telecoms, construction/urbanism, and health. The in-demand jobs include industrial maintenance, QHSE, data planning, contract lawyers, and specialized nurses.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”How can a candidate prepare effectively?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”Target certifying skills (HSE, ISO, CMMS), strengthen languages, and follow ANAPEC guides. Health competitions and recruitments by organizations like the CNSS remain solid entry points.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”Should companies adapt their HR policies?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”Yes, with quarterly compliance reviews, risk mapping integrating the Sahara context, and ESG provisions. International mobility and employer branding become pillars.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What role do territories play in job creation?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”Local authorities and State services, supported by the UN orientation, launch recruitments in health, education, equipment, and public management. Service quality strengthens talent attractiveness and retention.”}}]}What does the American initiative at the UN change for the Moroccan labor market?
It brings political visibility to the file, placing autonomy under Moroccan sovereignty as a reference. This visibility encourages investments in the southern provinces and creates immediate needs in compliance, engineering, logistics, health, and services.
Which sectors will recruit primarily if the resolution progresses?
Port logistics, renewable energies, fisheries, telecoms, construction/urbanism, and health. The in-demand jobs include industrial maintenance, QHSE, data planning, contract lawyers, and specialized nurses.
How can a candidate prepare effectively?
Target certifying skills (HSE, ISO, CMMS), strengthen languages, and follow ANAPEC guides. Health competitions and recruitments by organizations like the CNSS remain solid entry points.
Should companies adapt their HR policies?
Yes, with quarterly compliance reviews, risk mapping integrating the Sahara context, and ESG provisions. International mobility and employer branding become pillars.
What role do territories play in job creation?
Local authorities and State services, supported by the UN orientation, launch recruitments in health, education, equipment, and public management. Service quality strengthens talent attractiveness and retention.
Comments are closed